Hoarseness

Abnormal changes in the voice are called “hoarseness.” When hoarse, the voice may sound breathy, raspy, strained, or show changes in volume or pitch (depending on how high or low the voice is). Voice changes are related to disorders in the sound-producing parts (vocal folds) of the voice box (larynx). While breathing, the vocal folds remain apart. When speaking or singing, they come together and, as air leaves the lungs, they vibrate, producing sound. Swelling or lumps on the vocal folds hinder vibration, altering voice quality, volume, and pitch.
Some common causes of hoarseness include:
- Acute Laryngitis
- Allergies
- Vocal Strain
- Benign Vocal Cord
- Lesions
- Laryngeal Cancer
- Vocal Cord Hemorrhage
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux
- Smoking
- Vocal Cord Paralysis/Weakness
- Neurological Disorders
- Thyroid Disorders
- Neck Trauma
Evaluation
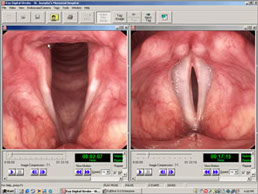
The specialists at New England ENT are skilled in quickly identifying your primary voice problem, and instituting prompt and effective therapy. Evaluation includes a thorough history of a patient’s hoarseness and general health, as well a complete ear, nose, and throat exam. The voice box is examined by means of a very small, lighted flexible tube (fiberoptic scope) that is passed through the nose to view the vocal folds. We also use the latest technology in Videostroboscopy, where the dynamics of the voice box is recorded and assessed in slow motion. These procedures are well tolerated by most patients. We work closely with Speech & Language Pathologists, who can also evaluate the voice to measure voice irregularities, how the voice sounds, airflow, and other characteristics that are helpful in diagnosing and guiding treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of hoarseness depends on the cause. Some basic recommendations include voice rest, improving hydration and taking medications to thin out mucus. Some patients are referred to Speech & Language Pathologists for Voice Therapy, which involves a combination of vocal exercises, breathing and muscle relaxation techniques. These “individualized” techniques are aimed to eliminate potentially harmful vocal behaviors, alter the manner of voice production, and/or enhance vocal fold tissue healing following injury. Emerging data suggest that voice therapy is an effective and appropriate method of therapy either in itself or as a compliment to other treatment modalities (eg, surgery, medications). The physicians at New England ENT are trained in phonomicrosurgery using microsurgical instruments, injectable fillers and laser technology to address conditions ranging from vocal cord paralysis to laryngeal masses/lesions.
Prevention Tips
- Quit smoking, and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Stay hydrated and avoid Alcohol and Caffeine.
- Humidify your home/work environment.
- Avoid straining your voice, and avoid whispering or singing when your voice is injured or hoarse.
- Watch your diet (avoid spicy foods) and manage reflux.
